Variable is a named value that can change. Actually Variables are used to store data temporarily. Variables will eventually enable us to do complex things. Using variable in
python is very simple. You have to give the name first for the variable, name can be anything.
Example:
saved_number = 5;
print(saved_number);
Output:------> 5





- Text Type: Str
- Numeric Types: int, float, complex
- Sequence Types: list, tuple, range
- Mapping Type: dict
- Boolean Types: Bool
- Set Types: set, frozenset
What are Quotation mark used for in python?
Quotation mark denote a string - a type of data in Python.
The following line of code prints the word print to the screen:
print("print")
print is an instruction,
"print" -is a data, which is a string. single quotes 'print' works too.
NOTE: Strings are a data type, not an instruction.
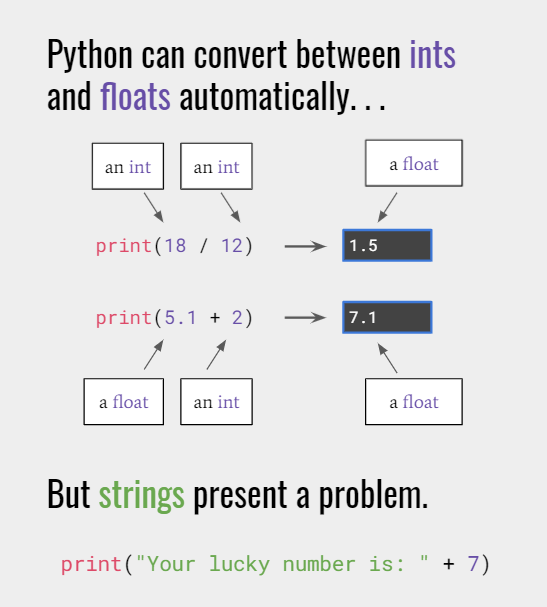
But strings aren't the only data type. Numbers are data too.
print(18)
Output: 18
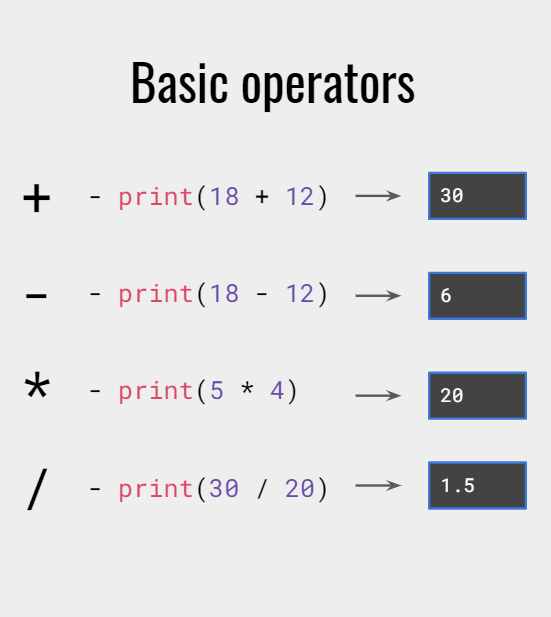
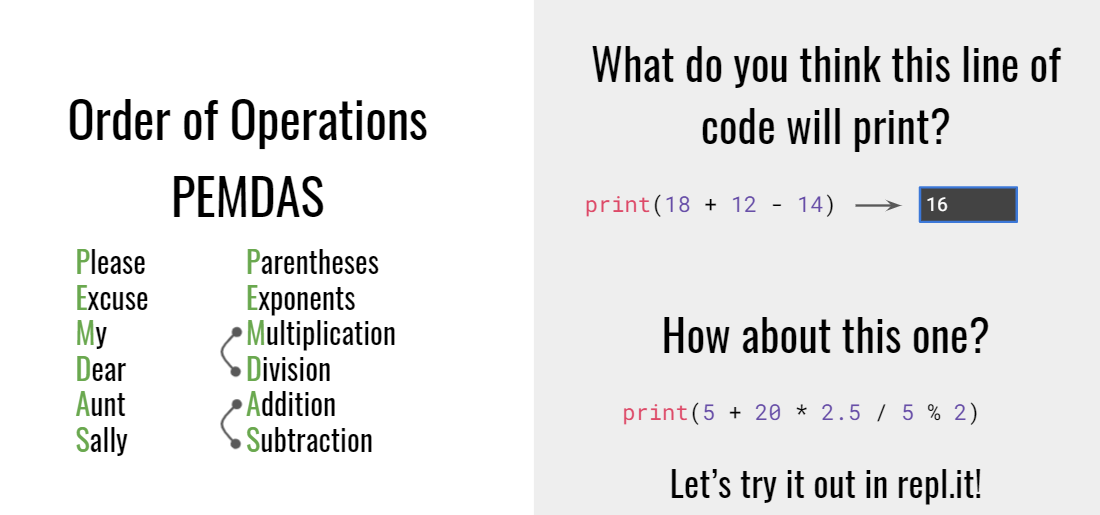
Numbersare data too, which means Python can do our math for us.
There are two numeric data types : int(Integer- a whole number) and float(Floating point- a number with a decimal point)



Getting the Data type
You can get the data type of any object by using the type() function:
Example:
Print the data type of the variable x:
x = 5
print(type(x))
Example:
Examples of data types:
string: "this is a string"
"25"
"Hello"
int: 1
25
463
float: 1.0
2.5
3.063
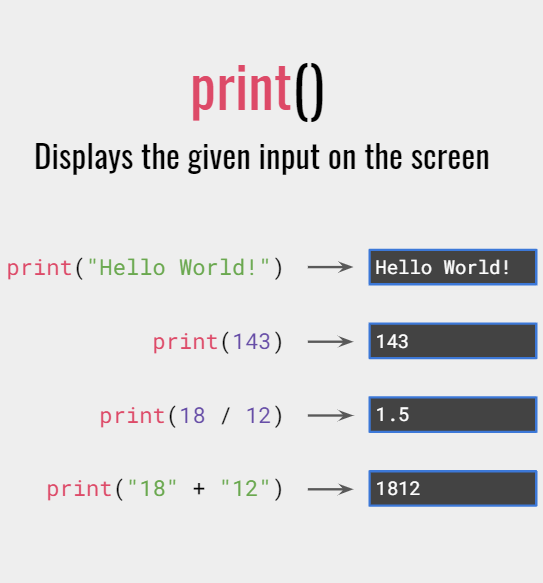
Python has a built in function, which we already discussed:
print()

Type Casting